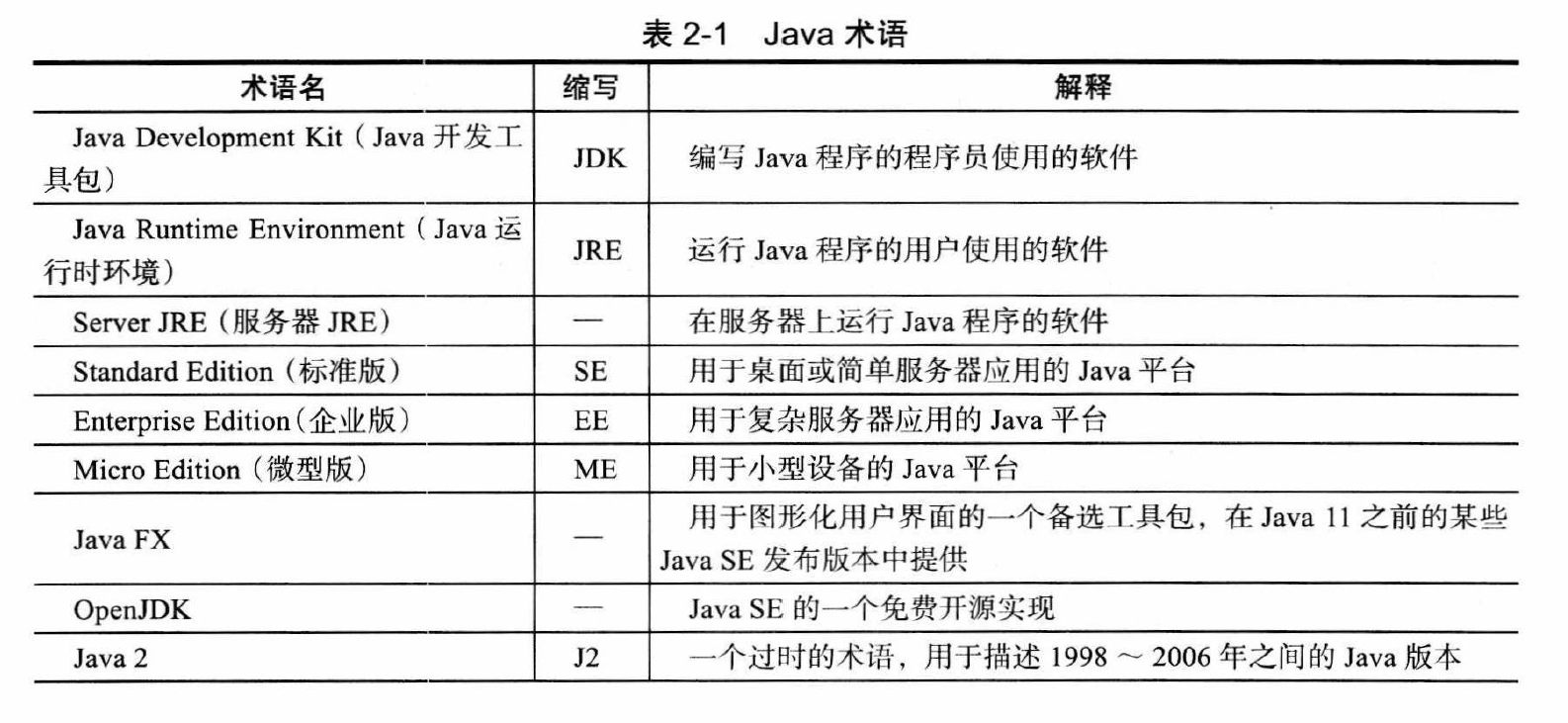
JAVA Open EXAM Study Chap1 概述 开发环境配置、环境变量、系统变量、编译是哪个、虚拟机是哪个? JAVA_HOME:JAVA安装目录
PATH:%JAVA_HOME%\bin
CLASSPATH:用户级类库
编译程序:JDK(含javac.exe和java.exe)
运行程序:JRE(含java.exe)
虚拟机:JVM
关系:
JVM+核心类库(lib/*.jar)=JRE
JDK>JRE>JVM
源文件后缀、中间字节码后缀? .java
.class
源文件命名?编译后出现几个字节码?
关于2):内部类也会生成class字节码文件,若为匿名内部类,则文件名="外部类"+"$"+num(该外部类的第几个内部类)+".class"
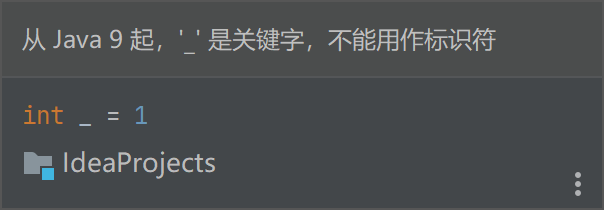
Chap2、3 语法 用户标识符命名规则?
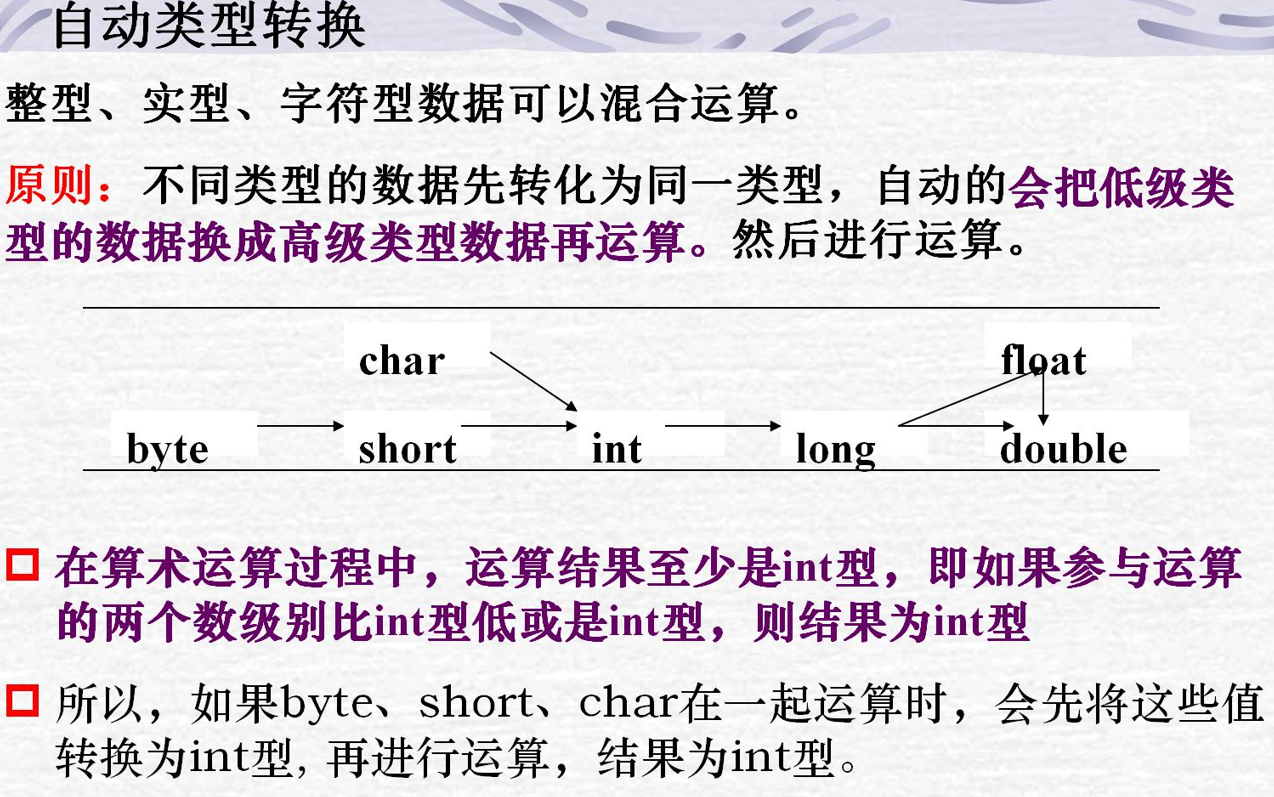
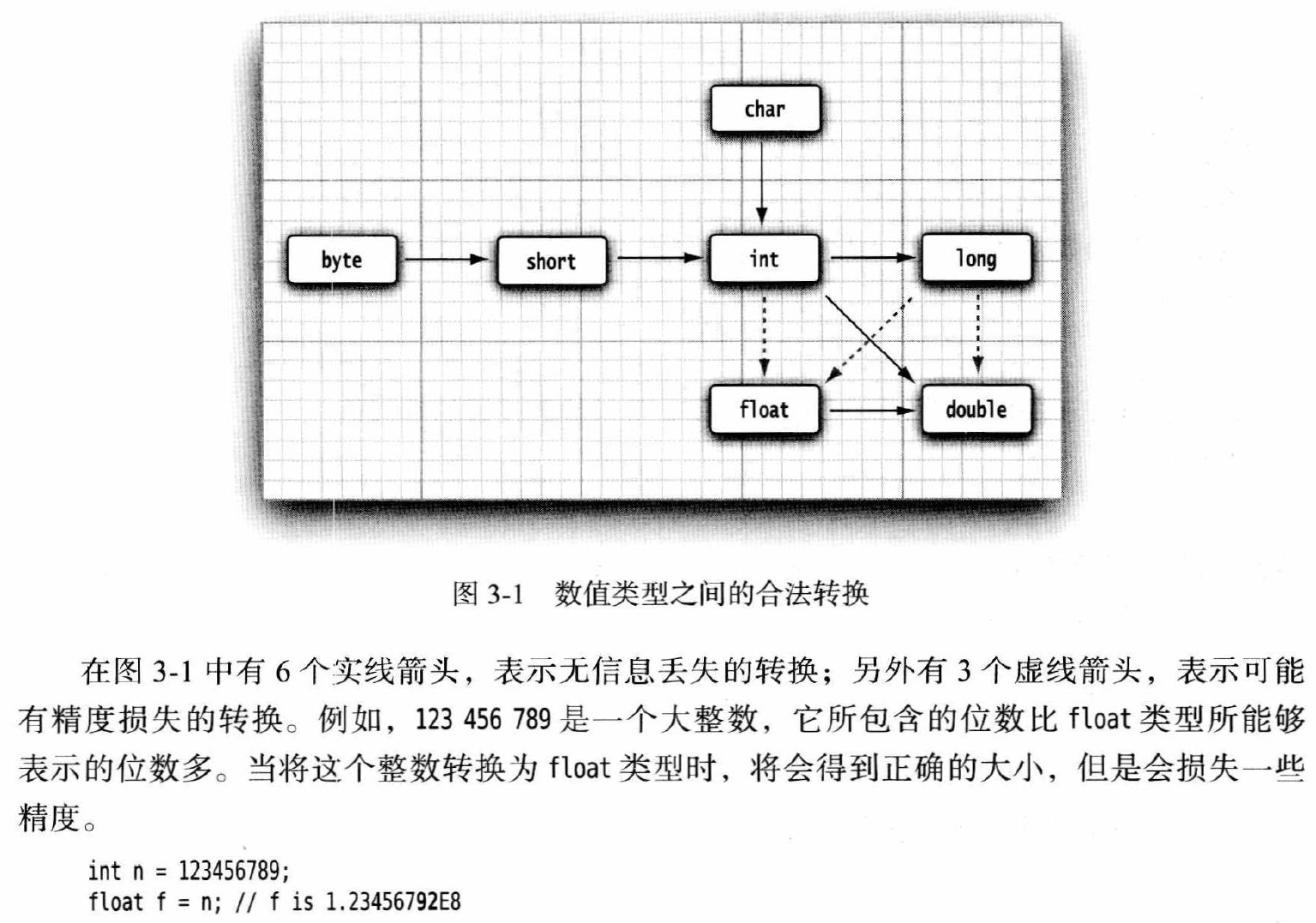
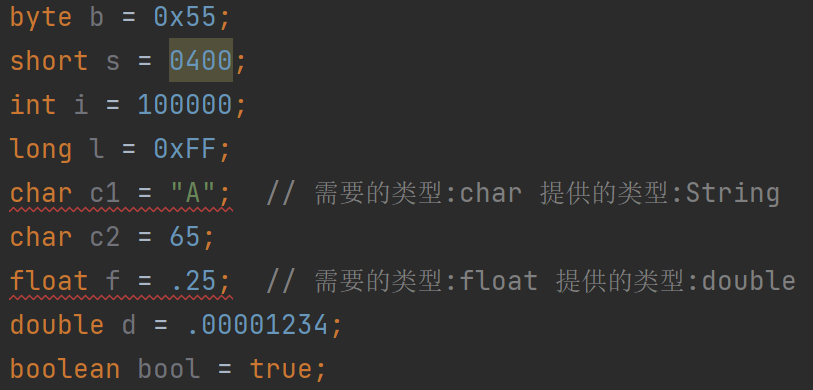
基本数据类型?类型转换? 8中基本数据类型及其存储需求、默认值。
类型转换:
隐式转换(自动转换)
更精确的隐式类型转换图
强制转换
(类型名)转换数值
数据作用域、初始化? 成员变量:编译器
形参:实参
局部变量、块变量:用户
数组初始化:基本数据类型为各自默认初始值,对象(Object)类型为null
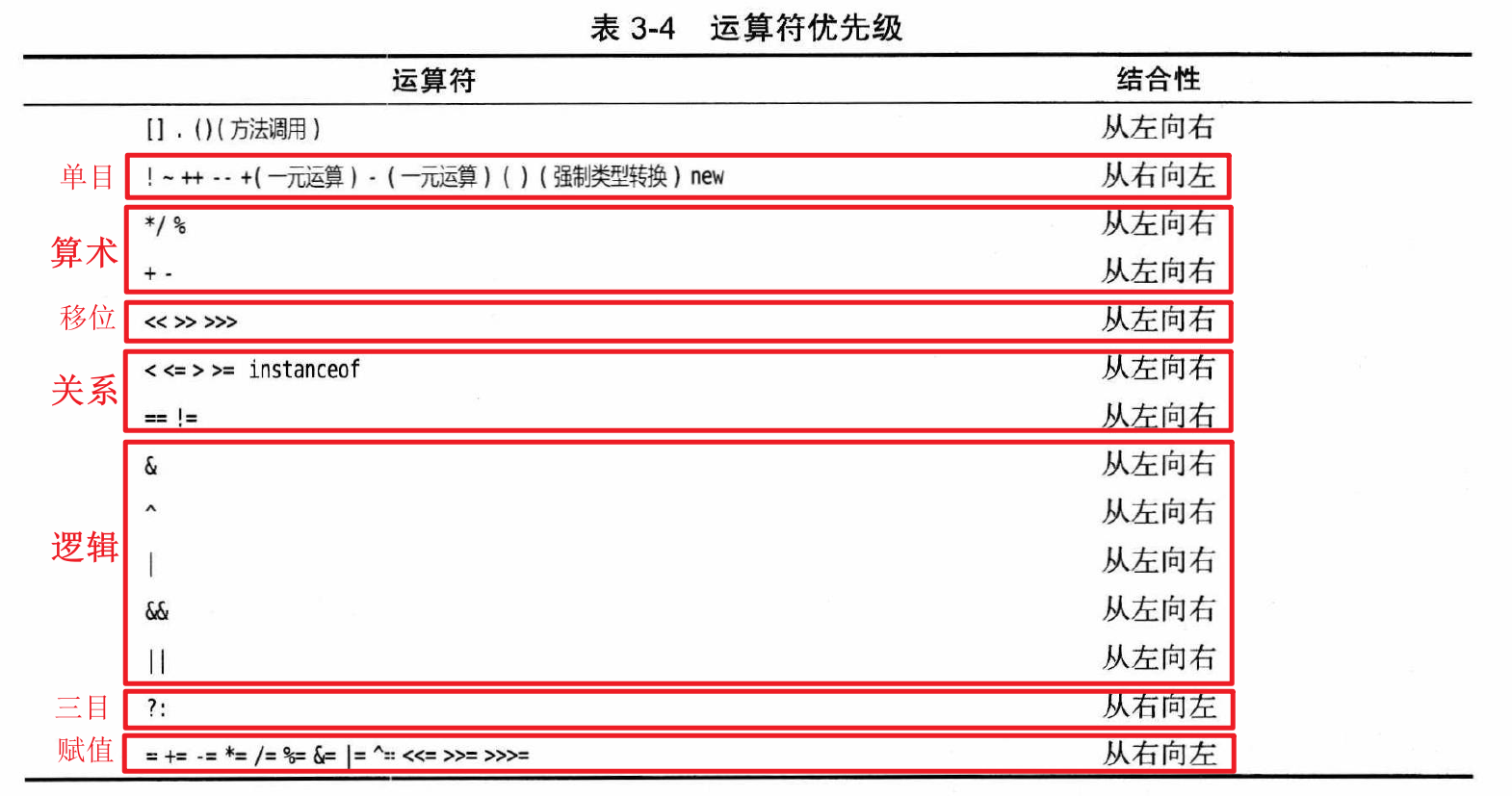
运算符? 优先级:单目 > 算术 > 移位 > 关系 > 逻辑 > 三目 > 赋值
参数传递 ?(函数栈帧)
画出主调方法和被调方法的栈帧,其中含有引用或值(基本数据类型)
画出堆(new出来的对象变量放这)或常量池(直接在代码中给出的变量放这,重复变量只放一个)
画出箭头将引用指向对应的变量
分析
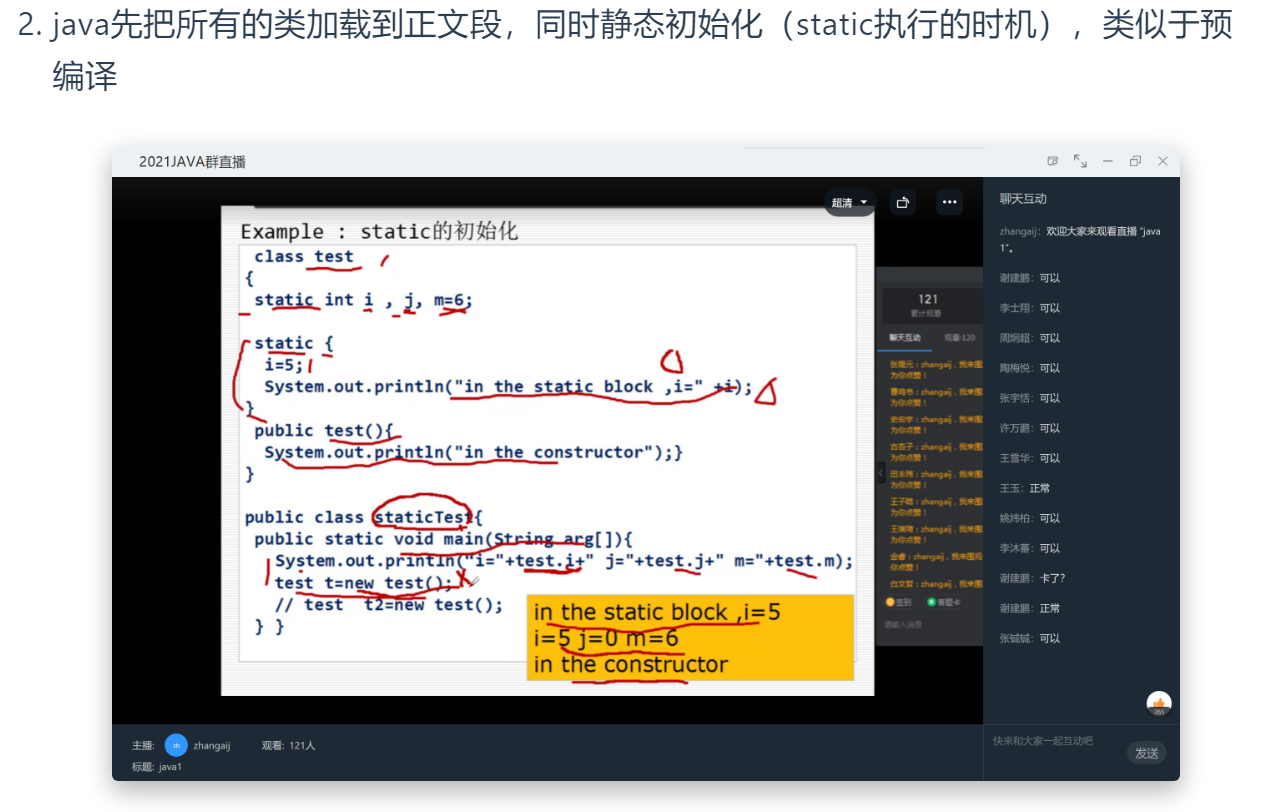
static执行的时机
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 package edu.wanpengxu.exam.grammar;public class Test3 { static int staticVar; int instanceVar; static void setStaticVar (int i) { staticVar=i; } void setVar (int i) { staticVar=i; instanceVar=i; } public static void main (String[] args) { System.out.println("staticVar=" +Test3.staticVar); setStaticVar(11 ); System.out.println("staticVar=" +Test3.staticVar); Test3 test3=new Test3 (); test3.setVar(13 ); System.out.println("staticVar=" +Test3.staticVar); System.out.println("test3's instanceVar=" +test3.instanceVar); } }
1 2 3 4 staticVar=0 staticVar=11 staticVar=13 test3's instanceVar=13
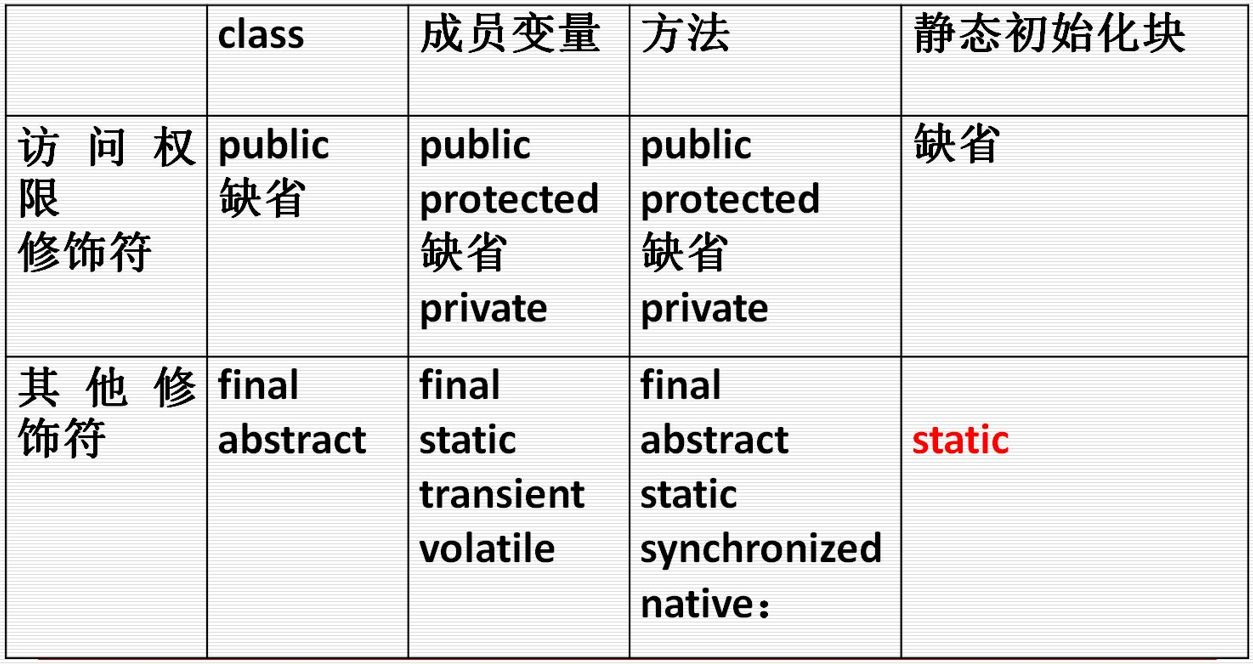
Chap4 面向对象 访问权限修饰符?非访问权限修饰符?
继承?多态?覆盖?重载? 子类可以继承父类的所有成员,但被private修饰的成员是不可见的。
在继承机制中,不允许在子类中降低成员(包括变量和方法)的访问权限。
如果子类中新定义的静态成员变量与父类中的某个静态成员变量同名,则这两个静态成员变量相互独立。
编译时类型由声明该变量时使用的类型(引用的类型)决定
运行时类型由实际赋给该变量的对象的类型(实例的类型)决定。
因为有编译时类型的限制,所以变量所调用的方法只能来自编译时类型的方法
覆盖:函数原型完全一致,即返回值类型、方法名、参数列表
重载:方法名相同而参数列表不同
对象初始化/实例化过程?(作业二)
注:1处不准确,若是第一次加载类
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 50 51 package edu.wanpengxu.exam.oop;class Log { public static String baseFieldInit () {System.out.println("Base Normal Field" );return "" ;} public static String baseStaticFieldInit () {System.out.println("Base Static Field" );return "" ;} public static String fieldInit () {System.out.println("Normal Field" );return "" ;} public static String staticFieldInit () {System.out.println("Static Field" );return "" ;} } class Base { static {System.out.println("Base Static Block 1" );} private static String staticValue=Log.baseStaticFieldInit(); static {System.out.println("Base Static Block 2" );} {System.out.println("Base Normal Block 1" );} private String value=Log.baseFieldInit(); {System.out.println("Base Normal Block 2" );} Base(){System.out.println("Base Constructor" );} {System.out.println("Base Normal Block 3" );} } public class Derived extends Base { static {System.out.println("Static Block 1" );} private static String staticValue=Log.staticFieldInit(); static {System.out.println("Static Block 2" );} {System.out.println("Normal Block 1" );} private String value=Log.fieldInit(); {System.out.println("Normal Block 2" );} Derived(){System.out.println("Derived Constructor" );} {System.out.println("Normal Block 3" );} public static void main (String[] args) { Derived d=new Derived (); } }
(1 2只在加载进正文段时执行一次)
父类static字段/块
子类static字段/块
子类构造方法进super(),父类构造方法进this(),父类非static字段/块(包括构造方法后的)
父类构造方法其余操作
子类构造方法super()结束,子类构造方法进this(),子类非static字段/块(包括构造方法后的)
子类构造方法其余操作
注:方法只有指名道姓时才会被调用。
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 Base Static Block 1 // 父类static Base Static Field // 父类static Base Static Block 2 // 父类static Static Block 1 // 子类static Static Field // 子类static Static Block 2 // 子类static Base Normal Block 1 // 父类非static Base Normal Field // 父类非static Base Normal Block 2 // 父类非static Base Normal Block 3 // 父类非static Base Constructor // 父类构造方法其余操作 Normal Block 1 // 子类非static Normal Field // 子类非static Normal Block 2 // 子类非static Normal Block 3 // 子类非static Derived Constructor // 子类构造方法其余操作
初始化过程常与动态绑定结合出题
如果通过子类构造函数调用父类构造函数(无论显示还是隐式),父类在构造时调用了被子类重写的方法,实际上调用的是子类覆盖的方法。
优点:通过继承相同的父类,初始化不同子类时,父类会调用不同的复写方法(真正new的那个子类的复写方法),从而实现多态性。 缺点:若是在父类构造函数中调用被子类重写的方法,会致使导致重写的方法在子类构造器的全部代码以前执行(子类构造函数在super()中,还没有this()),从而致使子类重写的方法访问不到子类实例变量的值,因为此时这些变量尚未被初始化。 (作业二)
作业二魔改版
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 50 51 52 53 54 55 56 57 58 59 60 61 62 63 64 package edu.wanpengxu.exam.oop2;class Base { private String name = "base" ; public Base () { tellName(); } public void tellName () { System.out.println("Base tell name: " + name); } } class Derived2 extends Base { private String name = "derived2" ; public Derived2 () { tellName(); } public void tellName () { System.out.println("Derived2 tell name: " + name); } } class Derived extends Base { private String name = "derived" ; public Derived () { tellName(); } public void tellName () { System.out.println("Derived tell name: " + name); } } class DerivedDerived extends Derived { private String name = "derivedDerived" ; public DerivedDerived () { tellName(); } public void tellName () { System.out.println("DerivedDerived tell name: " + name); } } public class Test { public static void main (String[] args) { new Derived (); new Derived2 (); new DerivedDerived (); } }
结果
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 Derived tell name: null Derived tell name: derived Derived2 tell name: null Derived2 tell name: derived2 DerivedDerived tell name: null DerivedDerived tell name: null DerivedDerived tell name: derivedDerived
流程:
new Derived(); Derived里的super( ) 进Base()Base里的this() :private String name = "base";,这时Base.name=”base”,Derived.name=nullBase里的其他 :tellName(),这个方法被主调类重写了,所以调的是Derived.tellname()Derived里的this() :private String name = "derived";,这时Base.name=”base”,Derived.name=”derived”Derived里的其他 :tellName(),自己就是将其重写的主调类,所以调的是Derived.tellname()new Derived2(); …
其他流程都差不多,要注意的是父类构造函数调的方法一定是被真正new的子类重写的
接口?抽象类? 详见课后小结
接口:interface
接口是对希望符合这个接口的类的一组需求 。
接口没有实例。
接口中的所有方法都是public,所有字段都是public static final
实现接口的类若非抽象类,则必须实现接口中的所有方法
实现接口时必须将方法声明为public,因为缺省访问权限为包内权限,编译器会报错,认为你试图提供更严格的(更弱的)访问权限
当方法冲突时:
超类冲突,超类优先
接口冲突,抛给程序员解决
使用{接口名}.super.{方法名}解决冲突
接口可以使用extends多继承
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 package edu.wanpengxu.exam.grammar;interface A { void displayA () ; } interface B { void displayB () ; } interface C extends A , B { void displayC () ; } public class Test4 implements C { @Override public void displayA () { System.out.println("This is interface A's implement." ); } @Override public void displayB () { System.out.println("This is interface B's implement." ); } @Override public void displayC () { System.out.println("This is interface C's implement." ); } public static void main (String[] args) { Test4 test4 = new Test4 (); test4.displayA(); test4.displayB(); test4.displayC(); } }
抽象类:abstract
可以提供方法实现
修饰符任意
抽象类也只能被单继承
内部类?匿名内部类? 内部类(inner class):定义在另一个类中的类。
使用内部类的原因:
内部类可以对同一个包中的其他类隐藏
内部类方法可以访问外围类的作用域中所有的数据,包括原本私有的数据
便于回调
语法格式
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 class OuterClass { class InnerClass { } } Copy
内部类与外围类的字段、方法处于相同地位(都是外围类的成员)
内部类可以直接访问外围类成员
匿名内部类
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 package edu.wanpengxu.course.anonymousinnerclasstest;class Class1 { public void display () { System.out.println("I am Class1" ); } } class Class2 extends Class1 { @Override public void display () { System.out.println("I am Class2" ); } } public class Test { public static void main (String[] args) { Class1 commonClassObject = new Class2 (); commonClassObject.display(); Class1 anonymousInnerClassObject = new Class1 () { @Override public void display () { System.out.println("I am Class3" ); } }; anonymousInnerClassObject.display(); } }
Chap5 异常 异常处理机制? 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 try { ... } catch (Exception e) { ... } finally { ... }
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 package edu.wanpengxu.exam.exception;public class Test { public static void main (String[] args) { try { System.out.print('a' ); method1(args); System.out.print('e' ); } catch (Exception e) { System.out.print('m' ); } System.out.print('f' ); } static void method1 (String[] a) { try { method2(a); System.out.print('b' ); } finally { System.out.print('c' ); } System.out.print('d' ); } static void method2 (String[] a) { System.out.println(a[a.length]); } }
正常的结果abcdef,m和n作为捕获异常的标志
带注释,存在异常抛出
去掉注释,各try块正常接受异常
出现异常立刻中断,找本try块的catch、finally,如果没有被catch就往主调函数抛直到被catch或不能再抛而报错。
带资源的try
资源在try块结束后会自动关闭,不需要finally
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 try (FileInputStream fileInputStream = new FileInputStream ("file1.data" ); ObjectInputStream objectInputStream = new ObjectInputStream (fileInputStream)) { Equation equation = (Equation) objectInputStream.readObject(); System.out.println("已将文件\"file1.data\"中的byte数组反序列化为一元二次方程对象" ); equation.display(); } catch (IOException | ClassNotFoundException e) { System.out.println(e.getMessage()); }
1 2 3 try (Scanner scanner = new Scanner (System.in)) { ... }
声明语句? throws
1 public Equation (double a, double b, double c) throws AWrongException
抛出语句? throw
1 if (a == 0 ) throw new AWrongException ("二次项系数不能为0!" );
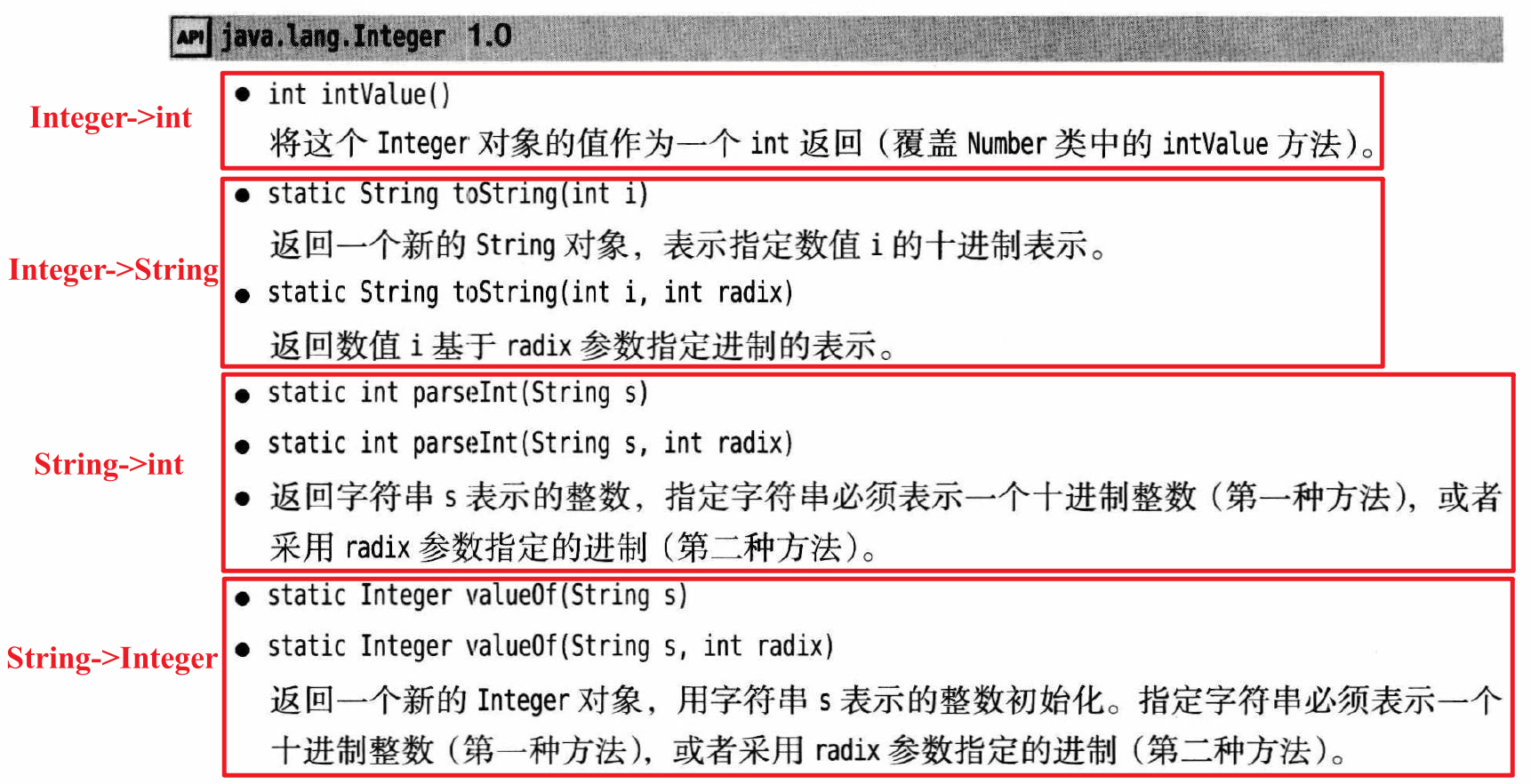
Chap6 核心类 包装类?:star:Interger
自动装箱
编译器 加上Integer.valueOf()
自动拆箱
编译器 加上.intValue()
Integer类的方法
直译
compareTo:比较
intValue:int型值
parseInt:转为int型
valueOf:取()作为Integer的值
toString:转为String型
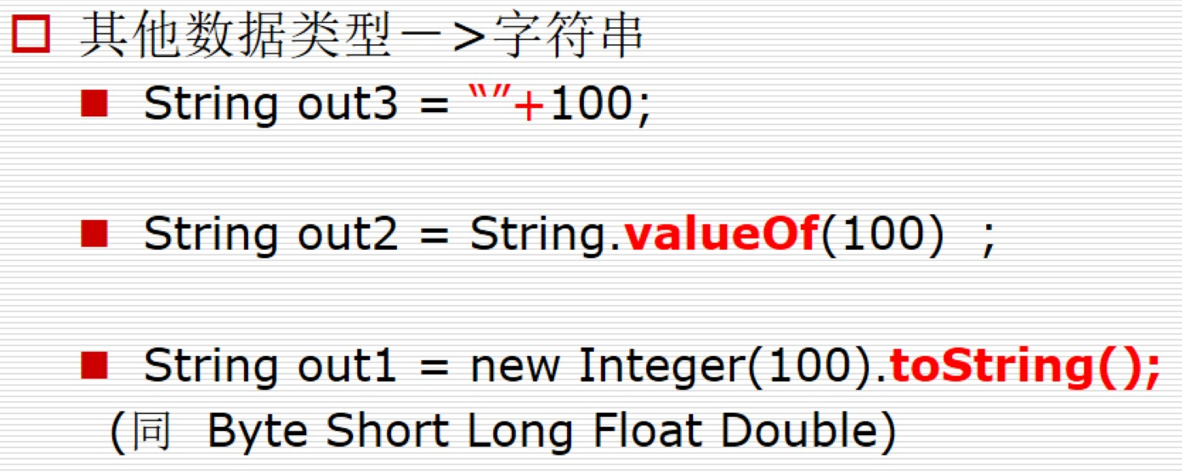
String?(除正则)
另,前两个方法应为:
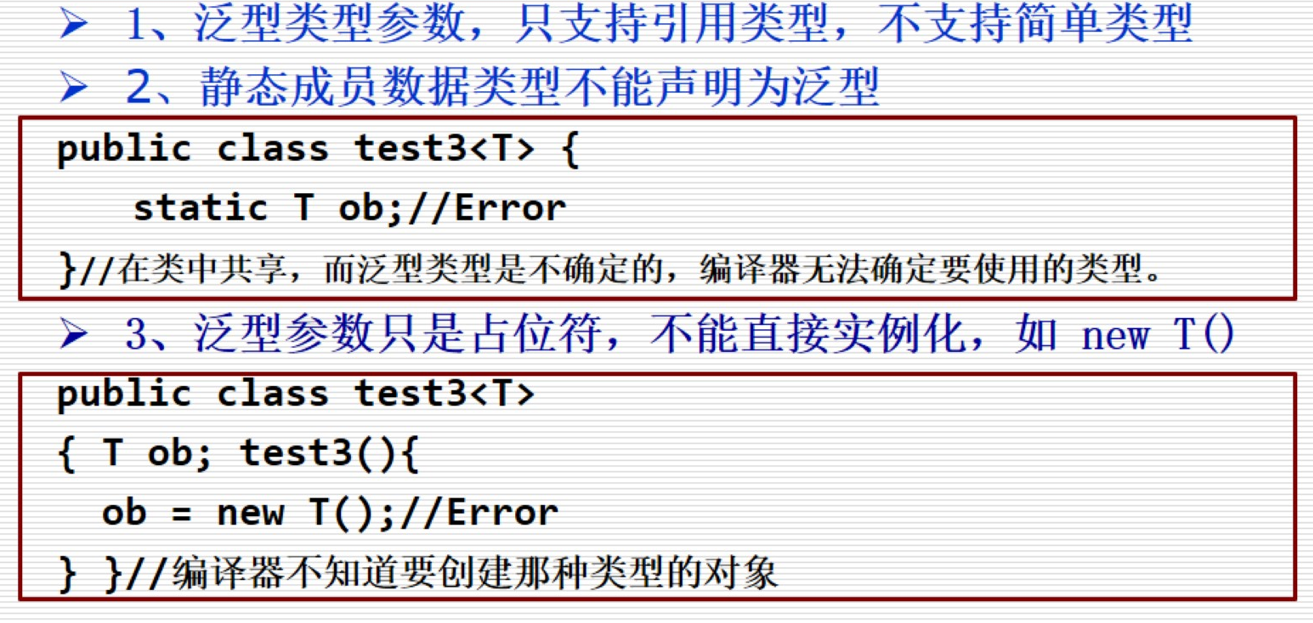
泛型类?(选择、考使用、遇到的问题) 泛型类:有一个或多个类型的类。
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 public class Pair <T> { private T first; private T second; public Pair () { first = null ; second = null ; } public Pair (T first, T second) { this .first = first; this .second = second; } public T getFirst () { return first; } public T getSecond () { return second; } public void setFirst (T first) { this .first = first; } public void setSecond (T second) { this .second = second; } }
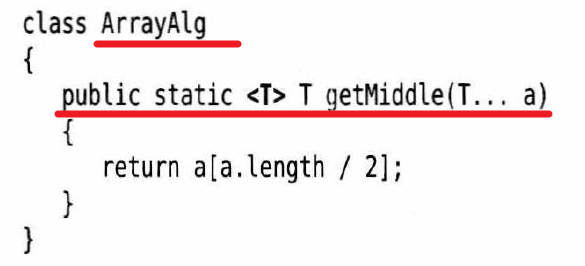
泛型方法
有界泛型
定义:
<T extends 类型1>:继承自类型1的任意类型T
使用:
<? extends 类型1>:继承自类型1的任意类型
<? super 类型1>:是类型1父类的任意类型
类型擦除
StringBuffer
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 public class Test { public static void main (String[] args) { StringBuffer stringBuffer=new StringBuffer ("2022年1月9日" ); stringBuffer.append("我" ); stringBuffer.append("学不完" ); stringBuffer.append("了" ); stringBuffer.delete(11 ,12 ); stringBuffer.insert(10 ,"终于" ); String string=stringBuffer.toString(); System.out.println(string); } }
IO? 节点流、包装流考1-2选择
略
Scanner要会应用。
Chap7 图形编程GUI 先把这几个包写上
1 2 3 import java.awt.*;import java.awt.event.*;import javax.swing.*;
创建GUI程序可以有两种思路
第一种是直接生成JFarme的实例,使用它自带的方法。(少)
第二种是写一个继承自JFarme的类(实名类或匿名类),按我们的需要重载它的方法,最后只需要一句话生成它的实例即可。(多)
第二种方法有一个好处是可以直接在类里调用方法,不用指定对象。
布局管理器有哪些?布局管理器怎么用?组件怎么放? 布局管理器有哪些?
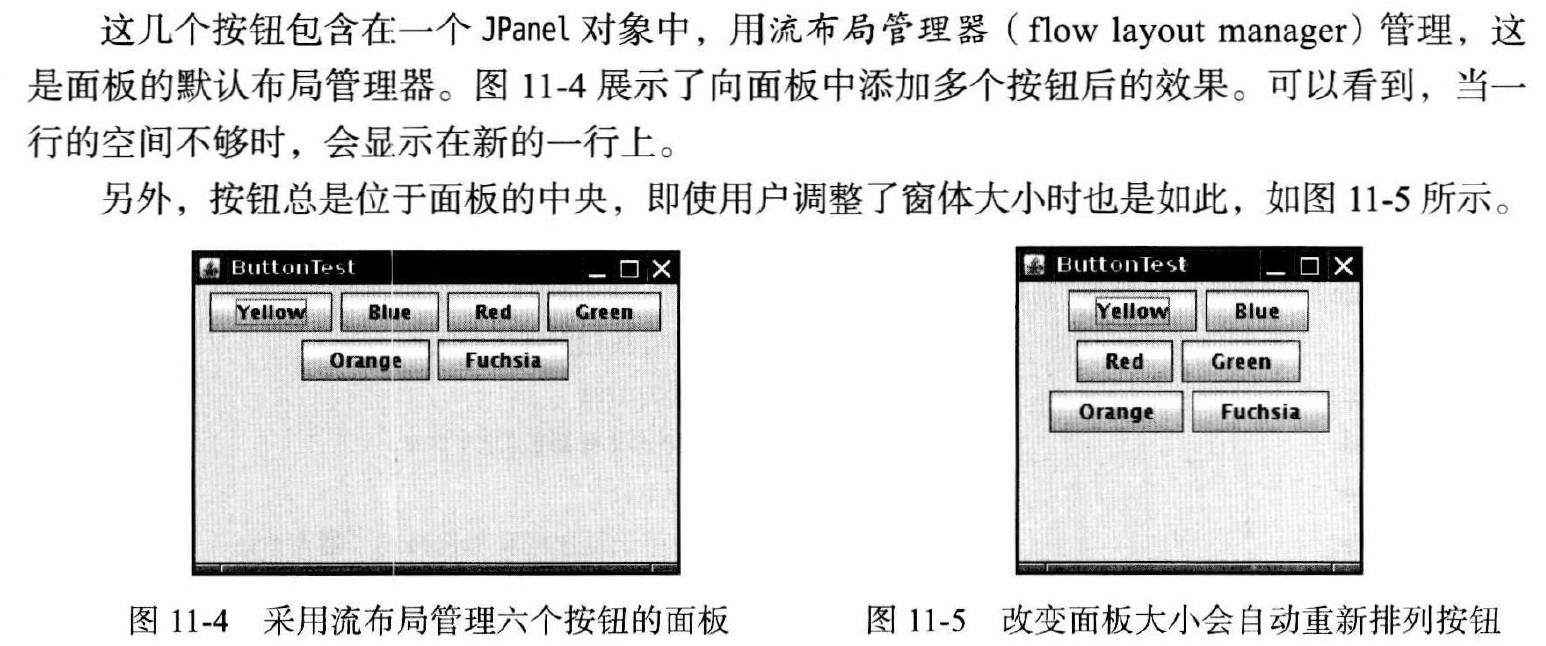
FlowLayout 流布局(Jpanel默认)
BoarderLayout 边框布局 (JFrame默认)
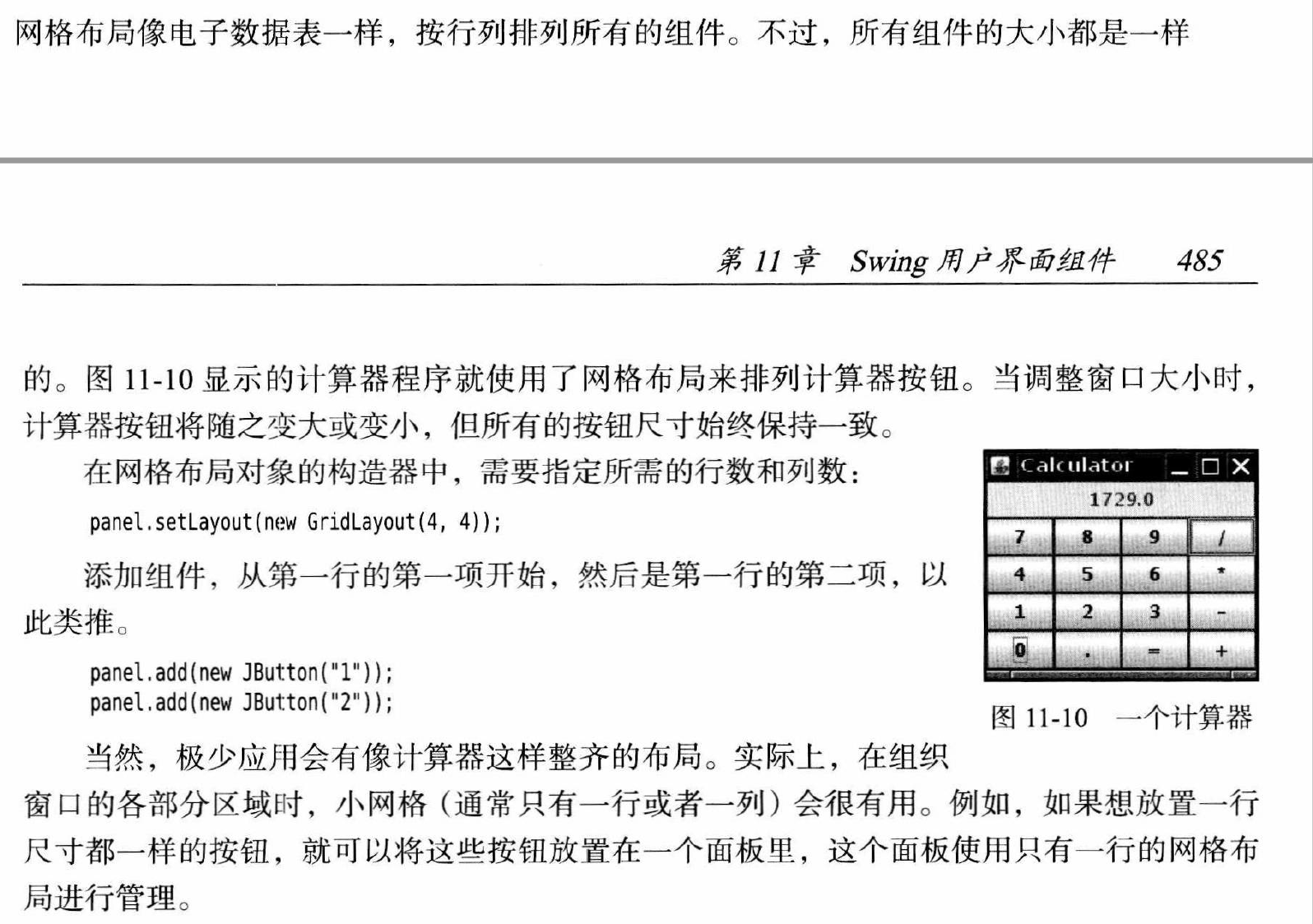
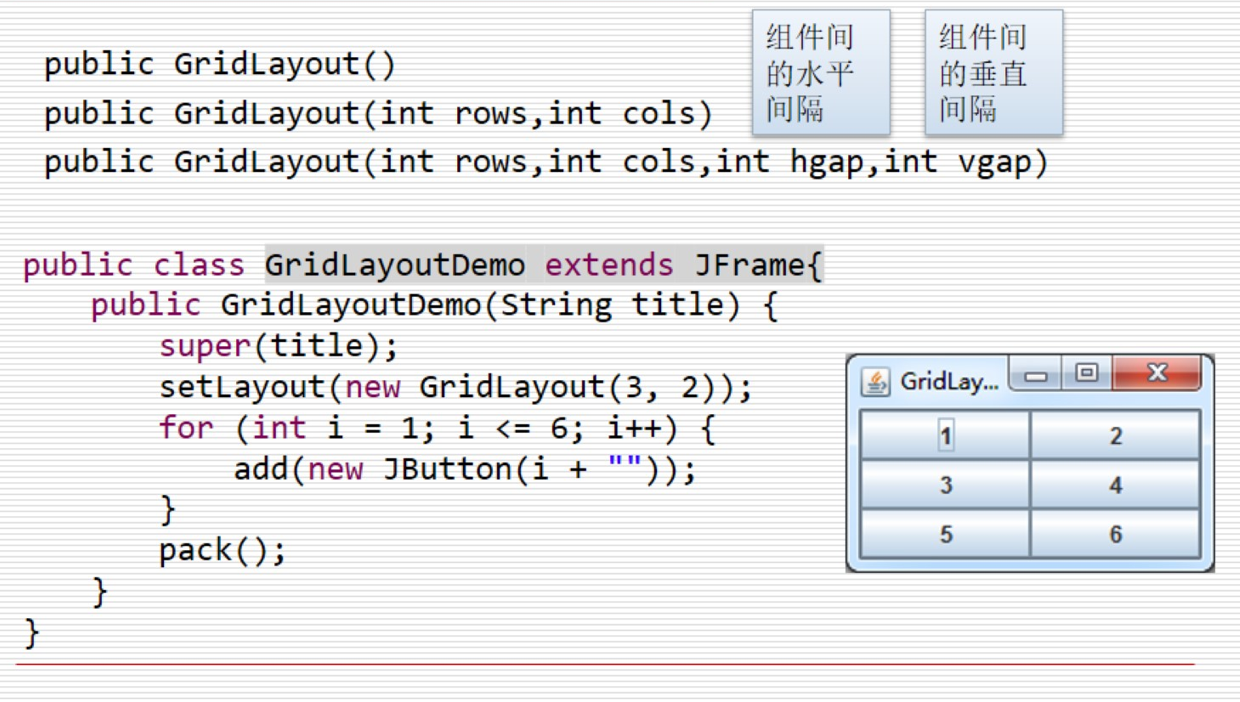
GridLayout 网格布局
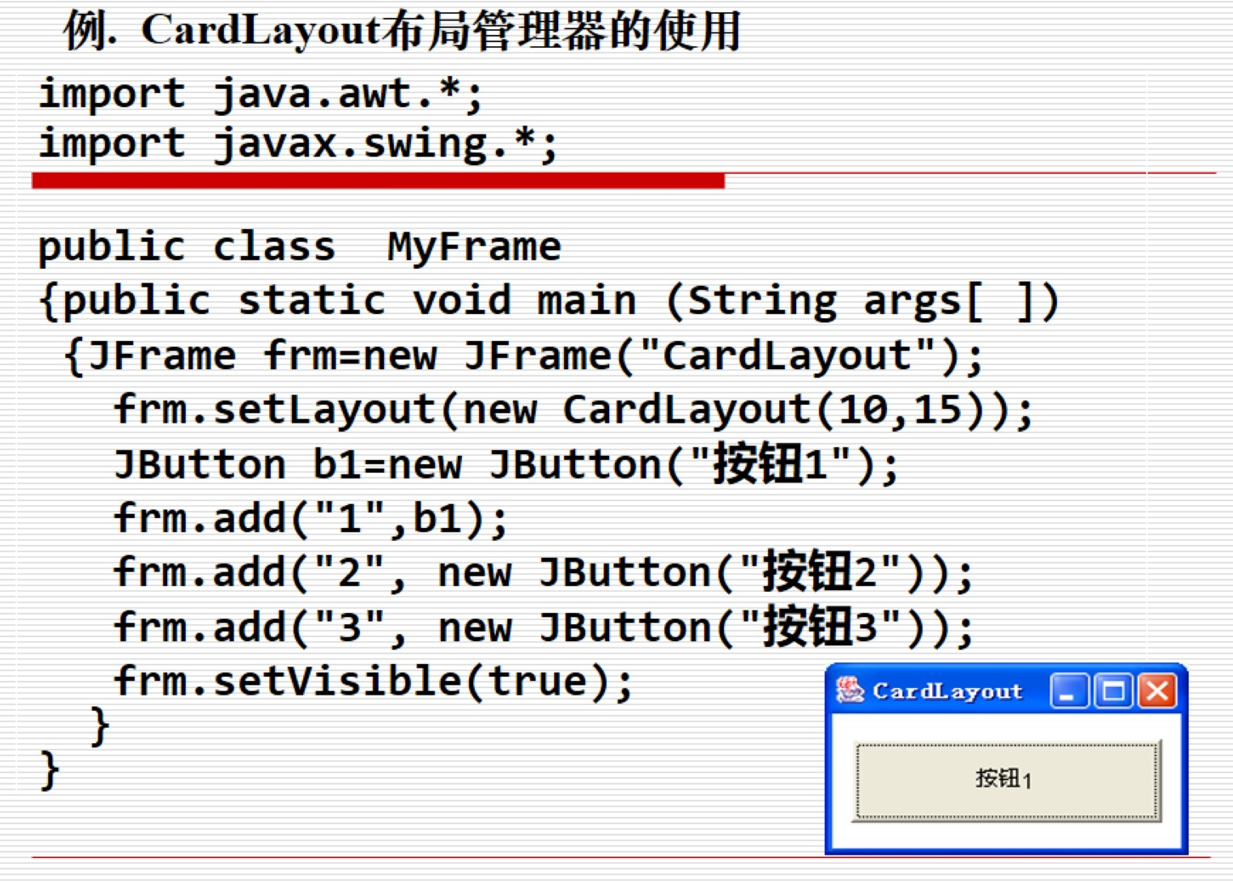
CardLayout 卡片布局
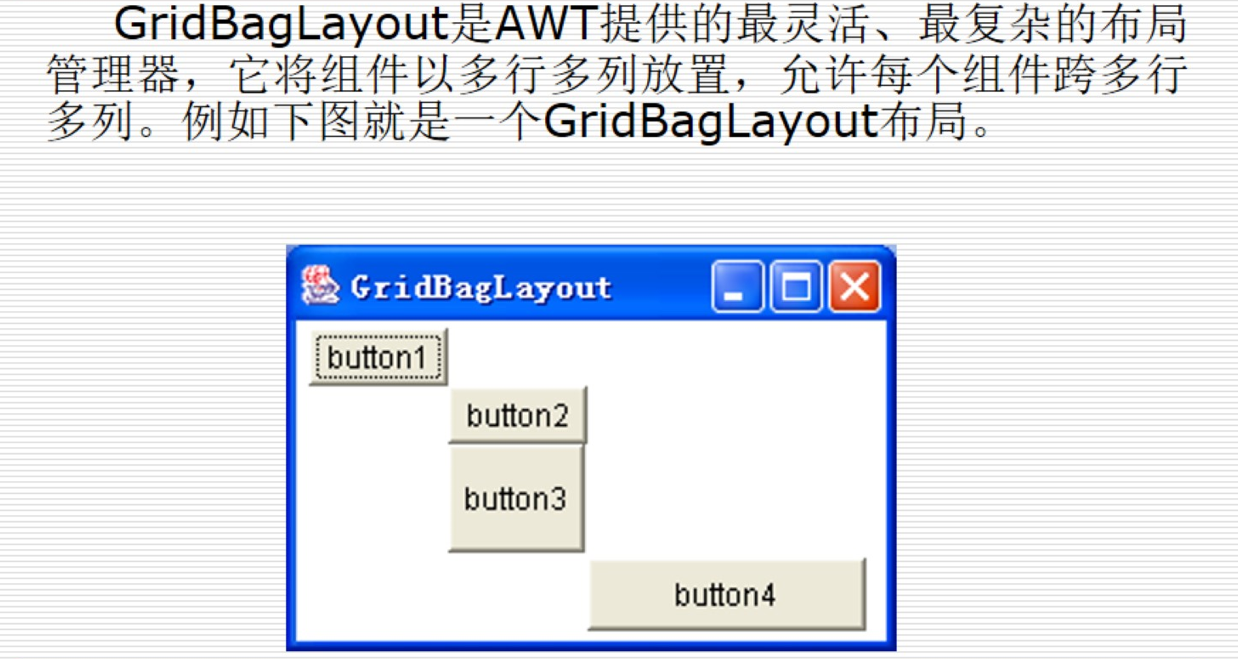
GridBagLayout
事件处理机制?(监听器)
对本类实现事件处理接口
使用匿名内部类 (多个方法,如鼠标事件MouseAdapter)/lambda表达式 (函数式方法,如按键事件ActionListener)
使用外部类
本质上都是往里传一个自定义了方法的类
绘制图像?(Paint(Grahpics g)、repaint()) 一个例子解决这些问题
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 50 51 52 53 54 55 56 57 58 59 60 61 62 63 64 65 66 67 68 69 70 71 72 73 74 75 76 77 78 79 80 package edu.wanpengxu.exam.gui;import java.awt.*;import java.awt.event.*;import javax.swing.*;public class GUIDemo extends JFrame implements ActionListener { boolean draw = false ; private JButton jButton1 = null ; private JButton jButton2 = null ; private JButton jButton3 = null ; private JButton jButton4 = null ; public GUIDemo (String title) { setTitle(title); setDefaultCloseOperation(JFrame.EXIT_ON_CLOSE); setLayout(new BorderLayout ()); setBounds(500 , 250 , 300 , 200 ); jButton1 = new JButton ("按钮1" ); jButton2 = new JButton ("按钮2" ); jButton3 = new JButton ("按钮1" ); jButton4 = new JButton ("按钮4" ); jButton3.setText("按钮3" ); add(jButton1, BorderLayout.NORTH); add(jButton2, BorderLayout.SOUTH); add(jButton3, BorderLayout.WEST); add(jButton4, BorderLayout.EAST); add(new JButton ("按钮5" ), BorderLayout.CENTER); jButton1.addActionListener(new ActionListener () { @Override public void actionPerformed (ActionEvent e) { jButton1.setEnabled(false ); } }); jButton2.addActionListener(e -> jButton2.setEnabled(false )); jButton3.addActionListener(e -> { draw = false ; JFrame jFrame = new JFrame ("图" ) { public void paint (Graphics g) { super .paint(g); g.setColor(Color.RED); if (draw) { g.drawOval(100 , 100 , 100 , 100 ); g.drawRect(300 , 100 , 100 , 100 ); } } }; jFrame.setBounds(200 , 200 , 500 , 300 ); jFrame.setVisible(true ); jFrame.addMouseListener(new MouseAdapter () { public void mouseClicked (MouseEvent e) { draw = true ; jFrame.repaint(); } }); }); jButton4.addActionListener(this ); setVisible(true ); } public void actionPerformed (ActionEvent e) { jButton4.setEnabled(false ); } public static void main (String[] args) { GUIDemo guiDemo = new GUIDemo ("考试" ); } }
Graphics g怎么画圆形?正方形? 1 2 3 4 5 6 public void paint (Graphics g) { super .paint(g); g.setColor(Color.RED); g.drawOval(x,y,w,h); g.drawRect(x,y,w,h); }
常用组件
JButton
无常用方法
JTextField
JLabel
JFarme常用方法
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 setTitle(title); setDefaultCloseOperation(JFrame.EXIT_ON_CLOSE); setLayout(new BorderLayout ()); setLocation(x,y); setSize(w,h); setBounds(x, y, w, h); add() setVisible(true );
Chap8 线程 线程类定义?(构造线程的方法?) 线程是一个继承自Thread的对象或一个实现了Runnable接口的对象
继承Thread
extends Thread
1 2 3 4 5 class myThread extends Thread { public void run () { } }
实现Runnable接口,通过Thread包装
implements Runnable
1 2 3 4 5 class myThread implements Runnable { public void run () { } }
开始线程
1 2 Thread t1 = new Thread (this );t1.start();
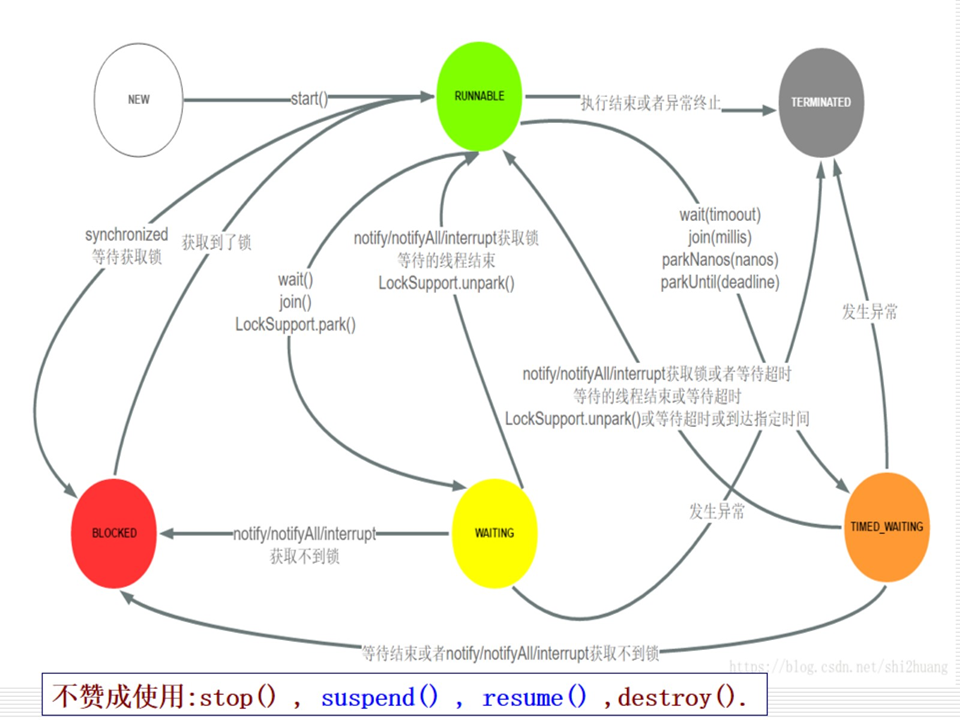
线程六态转换的方法? 线程的六种状态:
New 新建
Runnable 可运行
Blocked 阻塞
Waiting 等待
Timed waiting 计时等待
Terminated 终止
start:新建->可运行
yield:运行->可运行
stop:运行->终止
join:可运行->等待/计时等待
wait:挂起,可运行->等待/计时等待,只能因等待期满唤醒或被notify唤醒
notify:唤醒,等待/计时等待->可运行
sleep:暂停程序,运行->计时等待,睡眠期满时,等待->可运行 (仍要等待时间片)
计时等待都要指定参数
线程同步?(synchronized互斥) 同步方法
1 synchronized void get ()
同步语句块
1 2 3 4 5 void get () { synchronized (对象/类/this ){ ... } }
Guard.java
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 package edu.wanpengxu.exam.thread;public class Guard { private int value = 0 ; final String str = "" ; public void getValue () { synchronized (str) { System.out.println("=====start=====" ); System.out.println("get value is: " + value); } } public void setValue () { synchronized (str) { value++; System.out.println("value + 1: " + value); System.out.println("======end======" ); } } }
MyThread.java1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 package edu.wanpengxu.exam.thread;public class MyThread extends Thread { Guard guard; public MyThread (Guard guard) { this .guard=guard; } public void run () { for (int i=0 ;i<10 ;i++){ guard.getValue(); try { sleep(1000 ); }catch (Exception e){ e.getStackTrace(); } } } }
YourThread.java
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 package edu.wanpengxu.exam.thread;public class YourThread extends Thread { Guard guard; public YourThread (Guard guard) { this .guard=guard; } public void run () { for (int i=0 ;i<10 ;i++){ guard.setValue(); try { sleep(1000 ); }catch (Exception e){ e.getStackTrace(); } } } }
Test.java
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 package edu.wanpengxu.exam.thread;public class Test { public static void main (String[] args) { Guard guard=new Guard (); MyThread myThread=new MyThread (guard); YourThread yourThread=new YourThread (guard); myThread.start(); yourThread.start(); } }
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 =====start===== get value is: 0 value + 1: 1 ======end====== =====start===== get value is: 1 value + 1: 2 ======end====== =====start===== get value is: 2 value + 1: 3 ======end====== =====start===== get value is: 3 value + 1: 4 ======end====== =====start===== get value is: 4 value + 1: 5 ======end====== =====start===== get value is: 5 value + 1: 6 ======end====== =====start===== get value is: 6 value + 1: 7 ======end====== =====start===== get value is: 7 value + 1: 8 ======end====== =====start===== get value is: 8 value + 1: 9 ======end====== =====start===== get value is: 9 value + 1: 10 ======end====== 进程已结束,退出代码0